Curve Ball Physics
By:
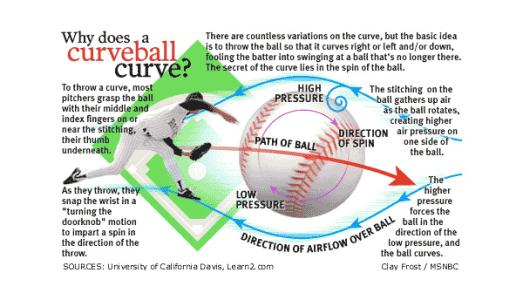
The secret to understanding a curveball is the speed of the air moving past the ball's surface. A curve has topspin, meaning that the top of the ball is moving in the same direction as the throw and the OPPOSITE direction of air flow relative to the direction of the throw. Vice versa for the bottom of the ball. It moves in the SAME direction as the air flow relative to the throw. See Bernoulli's principle, which says that the lower velocity of the air over the ball creates more pressure on the ball, which is what makes the curveball break downward. (Thanks to Lizbeth for correcting this info)
What difference does that make? The higher velocity difference puts more stress on the air flowing around the bottom of the ball. That stress makes air flowing around the ball "break away" from the ball's surface sooner. Conversely, the air at the top of the spinning ball, subject to less stress due to the lower velocity difference, can "hang onto" the ball's surface longer before breaking away.
As a result, the air flowing over the top of the ball leaves it in a direction pointed a little bit downward rather than straight back. As Newton discovered almost three hundred years ago, for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. So, as the spinning ball throws the air down, the air pushes the ball up in response. A ball thrown with backspin will therefore get a little bit of lift.
A major league curveball can veer as much as 171/2 inches from a straight line by the time it crosses the plate. Over the course of a pitch, the deflection from a straight line increases with distance from the pitcher. So curveballs do most of their curving in the last quarter of their trip. Considering that it takes less time for the ball to travel those last 15 feet (about 1/6 of a second) than it takes for the batter to swing the bat (about 1/5 of a second), hitters must begin their swings before the ball has started to show much curve. No wonder curveballs are so hard to hit.
One important difference between a fastball, a curveball, a slider, and a screwball is the direction in which the ball spins. (Other important factors are the speed of the pitch and rate of spin.) Generally speaking, a ball thrown with a spin will curve in the same direction that the front of the ball (home plate side, when pitched) turns. If the ball is spinning from top to bottom (topspin), it will tend to nosedive into the dirt. If it's spinning from left to right, the pitch will break toward third base. The faster the rate of spin, the more the ball's path curves.